The Ultimate Guide To Geotheta
The Ultimate Guide To Geotheta
Blog Article
The Main Principles Of Geotheta
Table of ContentsThe smart Trick of Geotheta That Nobody is Talking AboutAbout GeothetaExamine This Report about GeothetaGeotheta Things To Know Before You Get ThisThe 20-Second Trick For Geotheta
They conduct website investigations, gather samples, perform lab tests, and analyze information to examine the viability of the ground for building and construction jobs - Geotechnical Engineers. Based on their findings, geotechnical designers provide suggestions for structure layout, incline security, retaining structures, and mitigation of geotechnical hazards. They team up with other experts, such as engineers, architectural designers, and building teams, to make sure that geotechnical considerations are incorporated right into the total project style and application
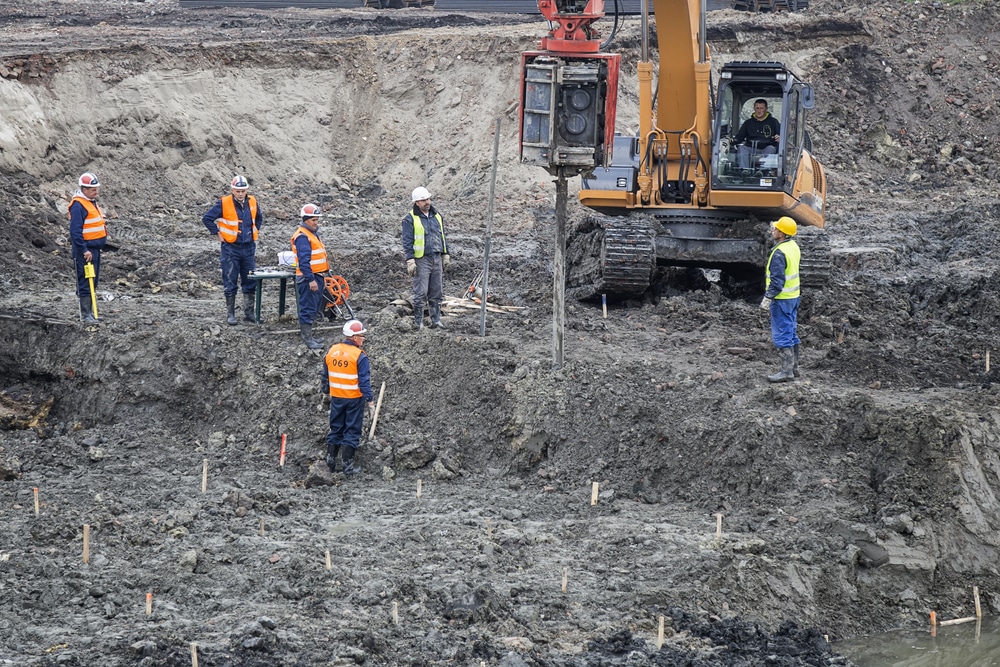
By analyzing the habits and residential or commercial properties of soil and rock, they can recognize prospective geotechnical risks such as landslides, dirt settlement, or incline instability. Their knowledge assists protect against failings or mishaps that can threaten lives and residential or commercial property. Right here are some detailed tasks and responsibilities of a geotechnical designer: Site Examination: Geotechnical engineers conduct site examinations to gather data on subsurface conditions.
They translate the information to recognize the residential or commercial properties and behavior of the soil and rock, including their strength, permeability, compaction features, and groundwater problems. Geotechnical Analysis and Layout: Geotechnical engineers evaluate the data accumulated throughout site investigations to assess the security and viability of the site for building jobs. They perform geotechnical estimations and modeling to assess elements such as birthing ability, settlement, slope security, side earth pressures, and groundwater circulation.
Geotheta Fundamentals Explained
Foundation Design: Geotechnical engineers play an important duty in developing foundations that can safely support the desired framework. They assess the dirt conditions and tons needs to figure out the suitable structure kind, such as shallow foundations (e.g., footings), deep structures (e.g (https://pxhere.com/en/photographer/4325446)., stacks), or specialized methods like soil enhancement. They take into consideration aspects such as settlement restrictions, bearing ability, and soil-structure interaction to develop optimum structure layouts
They evaluate construction strategies, monitor website activities, and perform field examinations to confirm that the layout recommendations are followed. If unforeseen geotechnical problems emerge, they examine the situation and give suggestions for removal or adjustments to the style. Threat Evaluation and Reduction: Geotechnical designers assess geotechnical threats and risks related to the project site, such as landslides, liquefaction, or soil erosion.

Collaboration and Communication: Geotechnical engineers work carefully with other experts associated with a job, such as engineers, structural designers, and building groups. Efficient interaction and collaboration are vital to integrate geotechnical factors to consider right into the general job layout and building process. Geotechnical designers offer technical knowledge, learn this here now solution queries, and guarantee that geotechnical demands are fulfilled.
The smart Trick of Geotheta That Nobody is Talking About
Here are some types of geotechnical engineers: Structure Engineer: Structure designers specialize in developing and assessing structures for frameworks. They evaluate the soil problems, lots requirements, and site qualities to figure out the most suitable foundation type and design, such as shallow foundations, deep foundations, or specialized techniques like stack structures.
They examine the aspects influencing slope stability, such as dirt buildings, groundwater problems, and incline geometry, and establish techniques to stop incline failures and mitigate risks. Earthquake Engineer: Earthquake engineers focus on examining and making frameworks to stand up to seismic forces. They assess the seismic risk of a site, evaluate soil liquefaction potential, and create seismic design criteria to make sure the security and resilience of frameworks during earthquakes.
They execute area testing, accumulate samples, and analyze the gathered information to define the soil properties, geologic developments, and groundwater conditions at a site. Geotechnical Instrumentation Engineer: Geotechnical instrumentation engineers concentrate on monitoring and measuring the habits of dirt, rock, and frameworks. They install and keep instrumentation systems that keep an eye on factors such as dirt settlement, groundwater levels, incline movements, and architectural variations to examine efficiency and provide early cautions of prospective concerns.
Little Known Facts About Geotheta.
They conduct tests such as triaxial examinations, debt consolidation tests, direct shear examinations, and leaks in the structure examinations to gather information for geotechnical evaluation and design. Geosynthetics Engineer: Geosynthetics engineers focus on the style and application of geosynthetic materials, such as geotextiles, geogrids, and geomembranes. They use these materials to enhance dirt stability, strengthen inclines, provide drainage options, and control disintegration.
They often tend to be investigative people, which suggests they're intellectual, introspective, and investigative. They are curious, methodical, logical, analytical, and sensible. Some of them are also social, meaning they're kind, charitable, participating, patient, caring, practical, understanding, sensible, and pleasant. Does this sound like you? Take our complimentary job examination to figure out if geotechnical engineer is just one of your top profession matches.
In the office environment, geotechnical designers make use of specialized software application devices to execute estimations, produce designs, and assess data. They prepare reports, testimonial job specifications, connect with clients and team participants, and coordinate task activities. The office setting offers a favorable atmosphere for study, evaluation, and cooperation with various other professionals involved in the task.
Our Geotheta Ideas
They often see job websites to perform site investigations, assess geotechnical conditions, and collect information for analysis. These brows through involve traveling to various areas, often in remote or challenging terrains. Geotechnical designers might perform soil tasting, conduct examinations, and display building activities to ensure that the geotechnical elements of the job are being implemented properly.
Geotechnical engineers also function in specialized geotechnical research laboratories. Geotechnical laboratory designers function thoroughly in these settings, managing screening tools, running tools, and videotaping information.
Report this page